From the moment oil first made it into the mainstream, peak oil and the imminent depletion of fossil fuels have been vehemently predicted.
From the moment oil first made it into the mainstream, peak oil and the imminent depletion of fossil fuels have been vehemently predicted.
A by-no-means exhaustive list of those predictions might run something like this:
“I take this opportunity to express my opinion in the strongest terms, that the amazing exhibition of oil which has characterized the last twenty, and will probably characterize the next ten or twenty years, is nevertheless, not only geologically but historically, a temporary and vanishing phenomenon – one which young men will live to see come to its natural end” (1886, J.P. Lesley, state geologist of Pennsylvania).
“There is little or no chance for more oil in California” (1886, U.S. Geological Survey).
“There is little or no chance for more oil in Kansas and Texas” (1891, U.S. Geological Survey).
“Total future production limit of 5.7 billion barrels of oil, perhaps a ten-year supply” (1914, U.S. Bureau of Mines).
“Reserves to last only thirteen years” (1939, Department of the Interior).
“Reserves to last thirteen years” (1951, Department of the Interior, Oil and Gas Division).
“We could use up all of the proven reserves of oil in the entire world by the end of the next decade” (President Jimmy Carter speaking in 1978 to the entire world).
“At the present rate of use, it is estimated that coal reserves will last 200 more years. Petroleum may run out in 20 to 30 years, and natural gas may last only another 70 years” (Ralph M. Feather, Merrill textbook Science Connections Annotated Teacher’s Version, 1990, p. 493).
“At the current rate of consumption, some scientists estimate that the world’s known supplies of oil … will be used up within your lifetime” (1993, The United States and its People).
“The supply of fossil fuels is being used up at an alarming rate. Governments must help save our fossil fuel supply by passing laws limiting their use” (Merrill/Glenco textbook, Biology, An Everyday Experience, 1992).
(Give particular heed to that last sentence.)
Quotes like these could fill hundreds of pages easily.
There comes a point, however — and we reached it long ago — when one needs to stop swallowing these scare-mongering scenarios.
There comes a point when one needs to look at the entire history of doomsday predictions and learn something from their long and undistinguished history of incontrovertible failure.
There comes a point, finally, when one needs to question what motivates these people.
To the millions of you who believe the latest round of dire forecasts, I ask you this in all seriousness:
What do you really think — that all the other apocalyptic predictions and predictors, over all the centuries and millennium, were wrong, but people like James Howard Kunstler and Richard Heinberg have at last got it right?
The fact is that anyone can say whatever he wants about anything. But that doesn’t necessarily make it true.
The 1970s book Limits to Growth, for instance, is chock full of reams of “hard data” proving mass famine and the end of the world as we know it — all to occur in a just couple of short decades from when it was written — but none of it came to pass. Not one word of it.
Thomas Malthus’s economic predictions of population-caused famines also failed stupendously, and Malthus himself — a guru of present-day environmentalists — eventually came to reject his early writings. No matter: This doesn’t stop neo-Malthusians like environmental high priest Lester Brown from forecasting a “2004 or 2005 worldwide famine.”
Or Dr. Paul Ehrlich of Stanford University laying “even odds that by the year 2000 Great Britain will no longer exist.”
Neither does it stop any of the endless predictions concerning global warming, species extinction, or forest depletion — for instance, the famous statement made by biologist Norman Myers, which sent environmentalists everywhere scurrying to their soapboxes, that “2 percent of all tropical forest was being destroyed per year,” and that by “2000 we will have lost a third of the world’s tropical forest” (Myers cited in Goudie 1993:46), which flew so far afield it would be laughable were it not so sickening.
(The Food and Agriculture Organization [FAO] puts tropical deforestation in the 1980s at 0.8 percent. In 2001, satellite imagery, which is precise, shows that tropical deforestation had declined to 0.46 percent.)
The history of humankind is replete with false prognostications. It’s time to ask why these predictions are not only always wrong but why they are always so spectacularly wrong.
Here is a crux:
In calculating the amount of natural resources, whether the resource is fossil fuel, crude oil, bauxite, bitumen, gold, or anything else, there is a vital principle at work; it is a principle that doomers of all persuasions have failed to discover and no longer, I think, have the capacity to grasp:
“No matter how closely it is defined, the physical quantity of a resource in the earth is not fully known at any time, because resources are sought and found only as they are needed. Even if the quantities of a particular resource were exactly known, such measurements would not be meaningful, because humans have a near-limitless capacity for developing additional ways to meet our needs: developing fiber optics, for instance, instead of copper wire …” (Julian Simon, The Ultimate Resource 2. Emphasis mine.)
The following is another secret about natural resources, which any legitimate graph or study will confirm:
The more a resource is used, the more that the supply of that resource increases.
It will sound counterintuitive, but only at first. Here’s why:
We begin to know about a resource only when we begin to use the resource. Knowing about that resource includes a cursory calculation of its quantity. The more we use of it, the more adept we become at finding it and calculating its quantity, extracting it and refining it. Thus, the more of it we use, the more of it we’re able to find.
The whole history of resource supply-and-demand has followed this exact principle.
Fossil fuel is no exception:
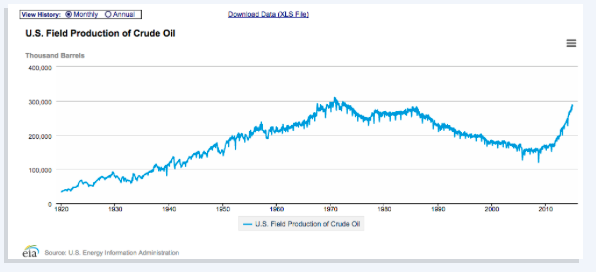
Observe any non-biased chart on the subject, and it will show that over the last century, oil supply has risen significantly, not diminished, as has virtually every other resource, so long as we’ve continued using it.
Quoting Peter Huber and Mark Mills:
Most of what people think they know about energy is so very wrong that their convictions, heartfelt though they may be, lie beyond logical contradiction or refutation….What most of us think about energy supply is wrong. Energy supplies are unlimited; it is energetic order that’s scarce, and the order in energy that’s expensive….Supplies do not ultimately depend on the addition of reserves, the development of new fuels, or the husbanding of known resources. Energy begets more energy; tomorrow’s supply is determined by today’s consumption. The more energy we seize and use, the more adept we become at finding and seizing still more.
What most of us think about energy demand is even more wrong. Our main use of energy isn’t lighting, locomotion, or cooling; what we use energy for, mainly, is to extract, refine, process, and purify energy itself. And the more efficient we become at refining energy in this way, the more we want to use the final product. Thus, more efficient engines, motors, lights, and cars lead to more energy consumption, not less (Peter Huber and Mark Mills, The Bottomless Well).
Some of the real data about fossil fuel is this:
Humanity consumes about 345 Quads of fossil fuel each year. A quad is a quadrillion British Thermal Units.
Of those 345 Quads, the United States consumes approximately 100.
The United States consumes by far the most, but — and here is a fact too often neglected in discussions of U.S. fossil fuel consumption — the United States also produces by far the most.
The inevitable exhaustion of fossil fuels, so strenuously predicted since the 1880’s, is a notion that’s invariably built upon a fraudulent premise: it’s built off the data of what today’s technology makes accessible.
This reasoning, as we’ve touched upon already, is demonstrably flawed.
No one seriously disputes that with better technology, and better power, we could retrieve far more [fossil fuel]. We already know where to find centuries’ worth of coal – global deposits hold 200,000 Quads. Oil shale deposits hold 10 Million Quads; heavy oils are already being extracted by brute force from the Canadian Athabasca deposits, and bioengineered bacteria could make the earth’s vast deposits of these oils economically accessible everywhere within a decade or less. Even more abundant is the energy locked up within uranium and other radioactive elements. The world’s oceans contain over 10 trillion Quads’ worth of deuterium, a fuel that we will in due course learn to unlock with nuclear fusion. And nothing very fundamentally new will be required to unlock it (Ibid).
Energy begets energy.
The more energy we use, the better we become at developing, extracting, and refining ever more.
Stopping or even slowing the use of fossil fuel would not, contrary to what you’ve been told, solve this (non-existent) fossil fuel problem: on the contrary, it would bring progress to a grinding halt; but even more than that, it would do so by shutting down the rational mind, which is the uniquely human method of survival.
It would blast us back to the stone age.
Which is precisely what many environmentalists, especially those of the better informed variety, want.
There exists no technology that can survey and measure the total quantity of oil and potential oil beneath all the land and sea, including tar sand and shale oil and the conversion of coal to oil.
So where exactly the doomers get their dire predictions is unclear.
What motivates these doomers is even more obscure.
And more frightening.
A quote from The Wall Street Journal, January 2005:
The cost of oil comes down to the cost of finding, and then lifting or extracting. First, you have to decide where to dig. Exploration costs currently run under $3 per barrel in much of the Mideast, and below $7 for oil hidden deep under the ocean. But these costs have been falling, not rising, because imaging technology that lets geologists peer through miles of water and rock improves faster than supplies recede. Many lower-grade deposits require no new looking at all.
To pick just one example among many, finding costs are essentially zero for the 3.5 trillion barrels of oil that soak the clay in the Orinoco basin in Venezuela, and the Athabasca tar sands in Alberta, Canada. Yes, that’s trillion – over a century’s worth of global supply, at the current 30-billion-barrel-a-year rate of consumption.
Please note particularly that last paragraph.
And, while you’re at it, do yourself another big favor:
Ignore all the dire predictions about peak oil and the end of fossil fuels that you’ve been hearing for the last one hundred years.
Ignore the catastrophic scare-mongering that books like The Party’s Over and The Long Emergency propound.
At every point in human history, the individual has been attacked by some government somewhere, on one side of the globe or another, always for the sake of some group.
In this century alone, to cite only a few of the more conspicuous examples, the individual was subordinated in Communist Russia to the proletariat; so too in Communist China, let us forget the millions upon millions of proletarians murdered or imprisoned under these romanticized regimes.
In Nazi Germany, the individual was subordinated to the “superior race.”
In Socialist Europe, in present day Germany and France, “labor” or the masses or The Environment all trump the individual.
In the United States as well claims concerning the environment threaten, as we speak, the individual’s right to her own life and property.
And the scare-mongering only increases: misinformation about fossil fuels has spawned, among a traditionally secular left, such a glut of doomsday predictions that they rival or eclipse any heard from the Religious Right — the only real difference being, instead of telling us to “repent, for the kingdom of heaven is at hand,” we’re told “learn to conserve and farm, for the end of the industrial society is at hand.”
But whether secular or non-secular, dogma is dogma, oppression is oppression, and the misguided doomsday predictions we hear from environmentalists are ultimately every bit as misbegotten as any doomsday predictions we hear from the Religious Right – and, one might well add, ultimately just as banal.
In one form or another, this propaganda is as old as mankind herself — the only real difference being the agenda.
Which agenda is this: let your big benevolent government regulate and control fossil fuels and all other energy besides, and let this same big benevolent government control your property as well, and thereby your life.
It’s called Environmentalism. But it’s really Neo-Marxism.
And Marxism by any other name is, and always will be, the same plain old discredited Marxism.